In WordPress, users often overlook speed measures in the dashboard. In this case – tweaking minor changes helps users quickly improve WordPress page speed.
In this article, you’ll learn about dashboard measures responsible for speed, performance, and page-level stats in WordPress.
You’ll also learn how to fix the WordPress dashboard and improve site speed without the developer’s assistance, expertise, or 3rd party plugins.
Factors That are Killing Your Site Speed
The following factors need consideration – when it comes to speed improvements in WordPress. We can certainly improve the following measures in a dashboard without prior experience with how WordPress works.
How to Improve WordPress Speed?
Improving page speed in WordPress requires the backend’s expertise. If you need more knowledge of WordPress, you should consult WordPress support services for speed optimization.
Here is, why contacting our plans for WordPress speed optimization and maintenance is the best option for beginners.
- We provide affordable plans for small, medium, and corporate websites.
- We have a plan for you – site recovery, speed optimization, and backup restoration – you’re in good hands.
- Create custom plans, and pay when you’re satisfied.
- Custom reports, improvements, and live sessions.
- One-time fixes, live support, or monthly plan for WordPress maintenance
Note: Before you’re ready, don’t forget to see our plans for WordPress speed optimization, support, and monthly plan.
Let’s proceed and learn about WordPress factors that affect your site’s speed.
1. Unmanaged Themes and Plugins
Managing WordPress themes and plugins requires no experience. However, if not handled correctly – it can create catastrophic consequences for WordPress maintenance.
As WordPress, by default, is packed with default Themes and Plugins, default assets from the WordPress dashboard need removal once you’ve installed your site’s favorite theme.
In the same manner – you should also update WordPress assets on Time. Here – unmanaged assets (Themes and Plugins) cause WordPress to pose in-compatibility issues – resulting in slow speed, errors, and maintenance issues.
Here is the case with page speed – after we’ve updated our site’s Themes and Plugins. The positive effect on speed helps users understand – how updating WordPress assets in the dashboard is essential.

To get started – head over to the Plugins and Themes page in the dashboard and – remove, update, or manage unused, outdated, and old assets with point-and-click options.
2. Unused Documents, Media, and 3rd party Files
Simply put – you shouldn’t host external files, media files, or 3rd party scripts on the WordPress dashboard, such as PDFs, non-supported media files, and ZIP packages.
Conversely – uploading 3rd party documents to the Hosting directory is ideal for speed. In this case – access levels, loading resources, and speed measures are handled only – when necessary and don’t cause a slow dashboard speed in WordPress.
For example – a place under (public_html) helps you store, access, and manage files – without loading an extra burden on the WordPress dashboard’s speed – as shown in the screenshot below.
Once you’ve created a directory under (public_html), use the Hosting cPanel’s upload option to upload external files. You can also use an FTP program for the said purpose – such as File Zilla.
Similarly, importing pre-made templates in WordPress, such as Themes’ layouts – results in a slow WordPress dashboard speed. If possible, once you’ve stopped using a specific Theme, make sure – you’ve removed media assets left behind in WordPress Media Library.
3. PHP Version
PHP is a scripting language that helps your site efficiently run PHP scripts, programs, and Apps. For example – WordPress is based on PHP and requires PHP installation on a server.
Specific scripts, programs, or 3rd party Apps may fail to achieve results – if your site’s PHP is not fully updated to the latest version.
For example – Divi Builder, a page builder for WordPress, fails to load its Builder if a site is running with an outdated version of PHP. Similarly, PHP needs the latest infrastructure for dashboard speed, WordPress performance, and maintenance.
For beginners – upgrading PHP on a server doesn’t ask for additional measures. Let’s learn how to update PHP’s version to the latest core.
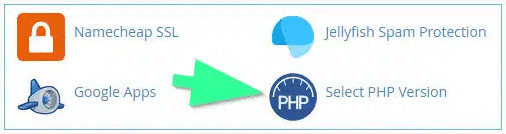
Your site’s Hosting cPanel options include an option to manage PHP versions, as shown in the screenshot below. However, if you lack Technical expertise in how things in cPanel work – you should ask for support from Hosting Support Representatives.
After you’ve completed updating the PHP version, you can confirm – if the process went normal. In the WordPress dashboard, the Site Health page helps you check the PHP version currently in place for your website, as shown in the screenshot below.

4. No Cache plugin installed on a WordPress website
A plugin for Cache helps you speed up the WordPress dashboard – no doubt. It also helps you cache site pages, resources, and CSS styles for improved performance, speed, and management.
The consequences of having no plugin installed for the WordPress cache can result in poor speed. In this case, let’s learn how to choose and install a cache plugin for WordPress.
You can find many candidates for WordPress cache in the WordPress plugins directory. Once logged into the WordPress dashboard, the Add New Plugin page helps you search for plugins, install, and activate a cache plugin with point-and-click options – as shown in the screenshot below.
Here – proceed with a plugin that best suits your WordPress installation. After you’ve installed one, the system, by default, configures basic cache routines for a WordPress website. You can also test your site’s speed after establishing a cache plugin, such as W3 Total Cache.
5. Time to First Byte (TTFB)
Time to First Byte depends solely on a Web Hosting server’s speed and configuration.
It refers to the time a server takes to respond, process, and return output to a user’s request. TTFB is usually measured in milliseconds, as shown in the screenshot below.
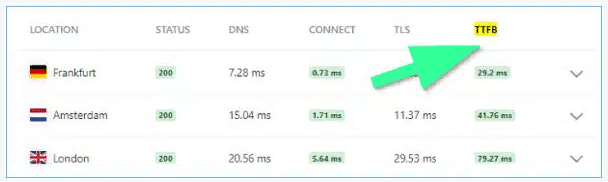
Here – a server taking longer to accept and respond to a user’s requests affects site speed measures. However – improving TTFB requires the developer’s assistance.
In this case, if you need more Technical expertise on how TTFB works for speed, you should hire WordPress maintenance services. Such services help you quickly fix speed issues without affecting the WordPress infrastructure your site relies on.
6. Screen options in WordPress Dashboard
The screen options section in the WordPress dashboard is a native feature and helps you show or hide WordPress widgets on the Home Feed.
For example – as shown in the screenshot below, you can hide WordPress widgets for activity, news, and posts.
As you install more plugins in WordPress, the number of widgets in screen options increases, which affects your dashboard’s speed.
There are two cases.
You should stop using unused plugins, if possible. You can also hide WordPress widgets for unnecessary options, helping you improve your dashboard’s speed in WordPress.
Let’s learn how to show or hide screen options in the WordPress dashboard.
Once you’ve logged into the WordPress dashboard, you can see the screen options at the top of the page.
For example – once you’ve installed security plugins for WordPress, such as WordFence, you can see its widget on the Home screen.
Similarly, in the WordPress dashboard, you can repeat the hiding process on Pages, Posts, and Category pages.
Note: If completing the above measures doesn’t improve your site’s dashboard speed, ensure you’re ready to proceed with a Technical audit of everything – including your site’s web hosting measures, images, and TTFB.
Note 2: After you make changes, make sure you check your site with GT Metrix, the tool for checking site speed measures, such as script loading, TTFB, and images that need optimization.
7. Optimize Images for Speed
Images bring life to your content and help boost engagement. Researchers have found that using colored visuals makes people 80% more likely to read your content.
However, if your images aren’t optimized, then they could be hurting more than helping. In fact, non-optimized images are one of the most common speed issues that we see on websites.
Before you upload a photo directly from your phone or camera, we recommend that you use photo editing software to optimize your images for the web.
In their original formats, these photos can have huge file sizes. But based on the image file format and the compression you choose in your editing software, you can decrease your image size by up to 5x.
There are widely 2 formats of images used: png and jpg(or JPEG)
Now you might be wondering: what’s the difference?
Well, the PNG image format is uncompressed. When you compress an image it loses some information, so an uncompressed image will be higher quality with more detail. The downside is that it’s a larger file size, so it takes longer to load.
JPEG, on the other hand, is a compressed file format that slightly reduces image quality, but it’s significantly smaller in size.
So how do we decide which image format to choose?
If our photo or image has a lot of different colours, then we use JPEG. If we need a transparent image, then we use PNG.
8. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
For example, let’s say your web hosting company has its servers in the United States. A visitor who’s also in the United States will generally see faster loading times than a visitor in India.
Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) can help to speed up loading times for all of your visitors.
A CDN is a network made up of servers all around the world. Each server will store “static” files used to make up your website.
These static files include unchanging files such as images, CSS, and JavaScript, unlike your WordPress pages which are “dynamic” as explained above.
When you use a CDN, every time a user visits your website they are served those static files from whichever server is closest to them. Your own web hosting server will also be faster since the CDN is doing a lot of the work.
You can see how it works in this infographic.

You can use CDN like Cloudflare.
It works well with WordPress websites and compliments your existing WordPress caching plugins for even faster loading times.
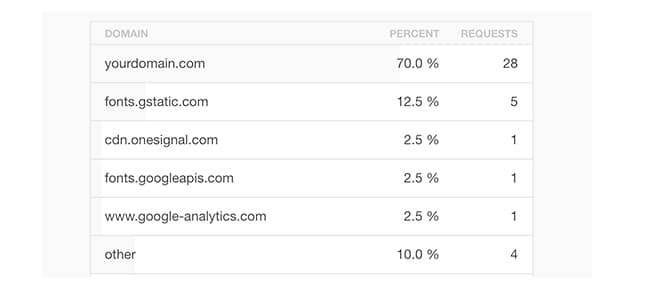
9. Reduce External HTTP Requests
Many WordPress plugins and themes load all kinds of files from other websites. These files can include scripts, stylesheets, and images from external resources like Google, Facebook, analytics services, and so on.
It’s ok to use a few of these. Many of these files are optimized to load as quickly as possible, so it’s faster than hosting them on your own website.
But if your plugins are making a lot of these requests, then it could slow down your website significantly.
You can reduce all these external HTTP requests by disabling scripts and styles or merging them into one file.
10. Reduce Database Calls

Unfortunately, there are a lot of poorly coded WordPress themes out there. They ignore WordPress standard practices and end up making direct database calls, or too many unnecessary requests to the database. This can really slow down your server by giving it too much work to do.
Even well-coded themes can have code that makes database calls just to get your blog’s basic information.
In this example, every time you see, that’s the start of a new database call:
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" dir="<?php language_attributes(); ?>">
<head profile="http://gmpg.org/xfn/11">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="<?php bloginfo('html_type'); ?>
charset=<?php bloginfo('charset'); ?>" />
You can’t blame theme developers for that. They simply have no other way to find out what language your site is in.
But if you are customizing your site using a child theme, then you can replace these database calls with your specific information in order to reduce all those database calls.
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" dir="ltr">
<head profile="http://gmpg.org/xfn/11">
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
Review your parent theme for instances like this that can be easily replaced with static information.
11. Limit Post Revisions
Post revisions take up space in your WordPress database. Some users believe that revisions can also affect some database queries run by plugins. If the plugin doesn’t specifically exclude post revisions, it might slow down your site by searching through them unnecessarily.
You can easily limit the number of revisions WordPress keeps for each article. Simply add this line of code to your wp-config.php file.
define( 'WP_POST_REVISIONS', 4 ); |
This code will limit WordPress to only save your last 4 revisions of each post or page, and discard older revisions automatically.
12. Use Lazy Loading if Needed
If you add many images, multiple video embeds, and photo galleries to your blog posts, then your site can benefit from lazy loading.
Instead of loading all your images and videos at once, lazy loading downloads only those that will be visible on the user’s screen. It replaces all other images and video embeds with a placeholder image.
As a user scrolls down, your website loads images that are now visible in the browser’s viewing area. You can lazy load images, videos, and even WordPress comments and gravatars.
Here are some of the lazy load plugins:
a3 Lazy Load
Lazy Loader
13. Use the Latest PHP Version
WordPress is mainly written in the PHP programming language. It is a server-side language, which means it is installed and runs on your hosting server.
All good WordPress hosting companies use the most stable PHP version on their servers. However, it is possible that your hosting company is running a slightly older PHP version.
The newer PHP 7 is two times faster than its predecessors. That’s a huge performance boost that your website must take advantage of.
You can see which PHP version your site is using by installing and activating the Version Info plugin.
Upon activation, the plugin will show your PHP version in the footer area of your WordPress admin dashboard.
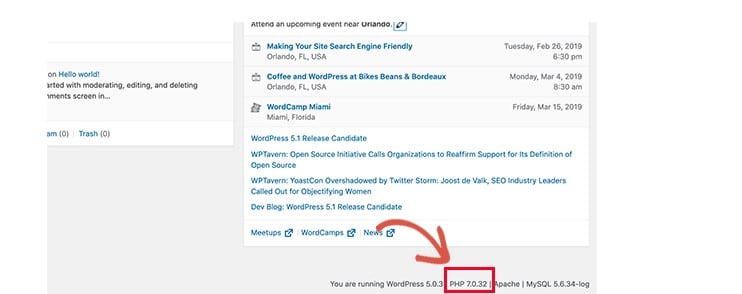
If your website is using a version lower than PHP 7, then ask your hosting provider to update it for you.
Conclusion
Assets in WordPress, such as Themes, Plugins, and 3rd party scripts – affect speed performance for pages, resources, and WordPress dashboards.
Installing a cache plugin for speed is undeniable in WordPress. Also – you need to keep your site’s PHP version up-to-date.
If you’d like to improve your site’s speed even more, improving your site’s TTFB is the best way. Keep in mind – enhancing TTFB asks for Technical expertise; proceed with caution.
For more information on improving your dashboard speed, let us help you fix things accordingly, from start to finish, with one-Time fixes, custom plans, or monthly routines for your WordPress website.





